How Face Recognition Works?
Face recognition is an advanced technology that utilises computer algorithms to verify or identify an individual by analysing facial features. The system compares a captured digital image or video frame with a database of facial data to determine if the two faces match. Facial recognition is not as accurate as fingerprint recognition, but it has become popular due to its non-invasiveness and convenience. Users don’t need to touch any surface, which makes it perfect for applications that prioritise hygiene, speed or comfort.
Face recognition has become a useful tool for a wide range of industries due to its contactless capabilities. It is used for device security, such as unlocking phones or authorising online purchases. It is used in law enforcement to identify suspects, track down missing people, and find individuals of interest. In the financial sector, it is also playing a greater role in digital authentication. This allows for a more secure and efficient verification of identity. Facial recognition will continue to gain popularity and influence how we interact in the digital world.
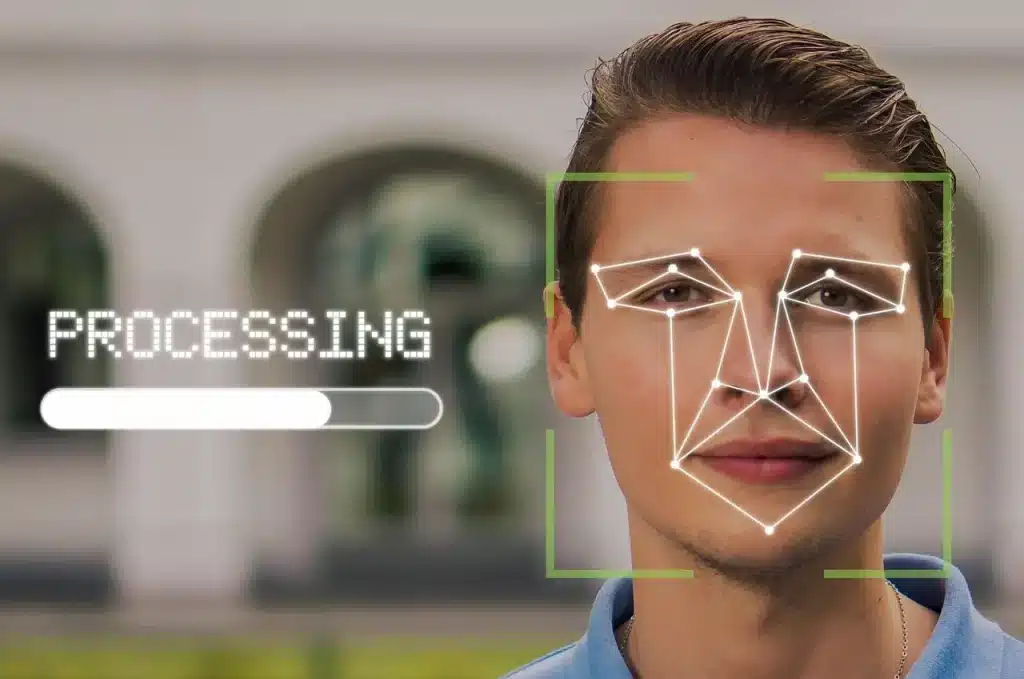
What is face recognition?
This type of biometrics analyses facial features to identify or verify a person. This technology compares the image of a captured face, whether it is from a video, photo or real-time feed, to a database of previously stored images. The speed and noninvasive nature of this tool have made it a popular tool for both the public and private sectors.
Facial recognition falls under the broader category of biometric authentication. This includes technologies such as fingerprint scanning, voice detection, and iris/retinal analysis. Facial recognition has many applications, including in law enforcement, security, consumer technology, marketing and healthcare.
History of Facial Recognition
In the 1960s, early attempts were made to create computer programs that could identify human faces. In 1964, computer scientists Woody Bledsoe and Helen Chan Wolf carried out pioneering work. They started manually mapping facial characteristics such as the distance between the eyes and the size of the mouth in order to differentiate individuals from each other within a database. However, much of their research was classified as it had been secretly funded and therefore, limited public access.
In the 1970s, the technology started to improve. In the 1970s, researchers began to incorporate additional facial features like hair colour and lip shape. They also used linear algebra models and became more prevalent in the decades that followed. These improvements allowed for a greater degree of accuracy when identifying people. In 2001, facial recognition was implemented by U.S. police during the Super Bowl XXXV held in Tampa, Florida. This marked a major turning point. The system scanned faces to identify individuals who could pose a danger. This was one of the very first public uses of facial identification.
How do Face Recognition Applications work?
The technology works by transforming facial features into data. This allows computers to verify or identify individuals. This process involves four stages.
Detection: The first step in detecting a face is to locate it within an image, a video or synchronised footage. Computer vision, a branch of AI that allows machines to interpret and analyse visual data, is used to achieve this. The system scans for facial patterns in the input and isolates these for further processing.
Analysis: After a face has been detected, the software analyses it by identifying approximately 80 distinct nodal points. These points are measurable features of the face, such as the width and shape of the nose. They also represent the distance between eyes, the depth of eye sockets, and the shape of the jawline. This step converts facial features into a unique digital representation.
Faceprint Storage and Creation: The nodal information is converted into a mathematical equation known as a “faceprint”, similarly to how fingerprints uniquely identify an individual. This faceprint, along with others, is stored in a database for comparisons.
Recognition: The system compares a faceprint with those stored in the database when a new image has been processed. If a match has been found, an individual’s identity may be flagged or confirmed, depending on the app.
Facial recognition systems are highly accurate when they have optimal conditions, even though they only rely on 80 nodal points. Accuracy can be affected if the face is partly obscured, turned sideways, or poorly illuminated. It is encouraging to see that improvements continue. According to the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology, the rate of false positives in facial recognition has decreased by half every 2 years since 1993.

What are the advantages of using facial recognition technology today?
The primary benefit of facial recognition is increased security. It can be used to monitor public areas, prevent unauthorised entry into secure areas and help law enforcement identify suspects or missing people. Face recognition has been used by airports, banks and prisons to improve security and streamline operations.
Facial recognition offers comfort. It allows users to unlock their smartphones or open apps without having to enter passwords. It can be used by social media platforms to organise or suggest tags for photos. The technology can be used to personalise customer experiences in retail and marketing by recognising returning customers or analysing demographics. Face recognition is expected to expand in its uses as it continues to develop, raising both ethical and legal questions.
Benefits of using Facial Recognition
Facial recognition offers many potential benefits. This includes enhancing security and authentication. Face recognition is a more hygienic and contactless alternative to biometrics that rely on contact, such as fingerprint scanners. These can fail if the person’s hands are dirty. In many scenarios, it is more secure than passwords and PIN codes, which can be seen by others. In some situations, iris scanning is more secure than facial recognition. However, it can be a good compromise between convenience and security. It can also be easily integrated into devices with front-facing cameras, such as smartphones or tablets, to provide quick and secure access.
The accuracy of facial recognition systems has been significantly improved by advances in machine learning, face mapping, and processing speed. Facial recognition can also be used to automate processes, such as airport check-ins. Passengers with biometric passports are able to skip long lines at the self-service kiosks and bypass lengthy queues. This streamlines travel and reduces wait times.

What are the uses of Facial Recognition?
Phone Security
Face recognition is used by many to unlock smartphones such as iPhones. It’s a safe and secure way to protect your data. Apple claims that there is only a one in one million chance of someone randomly unlocking your iPhone with Face ID. This makes it more secure than passwords.
Health Care Uses
Hospitals and clinics test facial recognition for accessing patient records, verifying identities and monitoring medication intake. The technology is also used to diagnose genetic disorders and detect pain levels.
Attendance Tracking
Facial recognition is a great way to automate attendance in schools and offices. In some countries, tablets are used to scan the faces of students and employees to verify their presence.
Law Enforcement
Facial recognition is used by police departments to match images from criminal databases with mugshots. By scanning faces on mobile devices and comparing the results to records in official databases, officers can identify suspects immediately.
Airports and Border Control
In airports, facial recognition has become commonplace. It speeds up the boarding process and improves security. Biometric passports enable travellers to bypass automated gates and improve identity verification at border crossings.
Finding Missing Persons
Facial recognition can be used by law enforcement to identify missing people or victims of human trafficking. They do this by comparing the faces of those individuals to public databases or surveillance footage. If matches are found in public areas like malls and airports, alerts can be sent.
Retail security and customer experience
Retailers can use facial recognition technology to prevent fraud and identify shoplifters. It can be used to personalise the shopping experience for customers by suggesting products or enabling face payment systems that allow them to bypass checkout lines.
Banking and Online Transactions
Biometric verification, instead of passwords, can be used to enhance online banking security. Liveness detection features ensure that only genuine users, not photos or fakes, can access accounts and approve transactions.




